Structure and motion of the atmosphere of the exoplanet Tylos
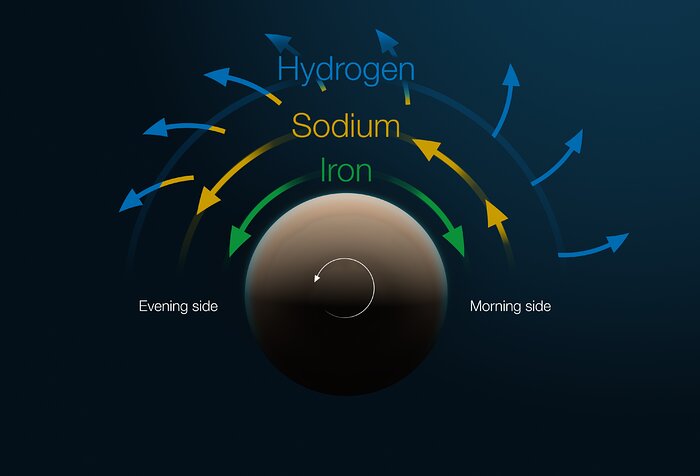
This diagram shows the structure and motion of the atmosphere of the exoplanet Tylos (WASP-121b). The exoplanet is shown from above in this figure, looking at one of its poles. The planet rotates counter-clockwise, in such a way that it always shows the same side to its parent star, so it's always day on one half of the planet and night on the other. The transition between night and day is the "morning side" while the "evening side" represents the transition between day and night; its morning side is to the right and its evening side to the left.
As the planet crosses in front of its host star, atoms in the planet’s atmosphere absorb specific colours or wavelengths of the star’s light, which can be measured with a spectrograph. From this data –– obtained in this case with the ESPRESSO instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope –– astronomers can reconstruct the composition and velocity of different layers in the atmosphere.
The deepest layer is a wind of iron that blows away from the point of the planet where the star is directly overhead. Above this layer there is a very fast jet of sodium that moves faster than the planet rotates. This jet actually accelerates as it moves from the morning side to the evening side of the planet. Finally, there is an upper layer of hydrogen wind blowing outwards. This hydrogen layer overlaps with the sodium jet below it.
Credit:ESO/M. Kornmesser
About the Image
| Id: | eso2504c |
| Type: | Artwork |
| Release date: | 18 February 2025, 17:00 |
| Related releases: | eso2504 |
| Size: | 4412 x 3000 px |
About the Object
| Name: | WASP-121 b |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Circumstellar Material : Planetary System |
| Category: | Exoplanets |